UIRIM NOTICE
NEWS&EVENTS
공지사항
ULTRIVA
주영오
2026-01-20
조회수 12
A thrombectomy is a medical procedure to mechanically remove a blood clot (thrombus) from a blood vessel, crucial for restoring blood flow in conditions like ischemic stroke, heart attack, or pulmonary embolism, using either minimally invasive catheter-based methods (aspiration, stent retrievers) or open surgery, often performed quickly to prevent severe damage.
Types
- Mechanical/Endovascular Thrombectomy: Minimally invasive, using catheters inserted via groin to reach the clot and remove it with suction, stents, or other devices.
- Surgical Thrombectomy: More invasive, involving open surgery to access and remove the clot from arteries or veins.
Common Uses
- Ischemic Stroke: Removing clots blocking brain arteries to save brain tissue.
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): Clearing clots from lung arteries to reduce heart strain.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Removing clots from legs to prevent complications like post-thrombotic syndrome.
- Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack): Clearing clots from heart arteries.
How it Works (Mechanical Thrombectomy)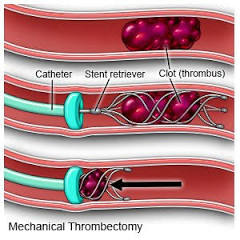

- Access: A catheter is inserted into a blood vessel (usually in the groin).
- Navigation: Guided by imaging, it travels up to the blocked vessel.
- Clot Removal: Devices like stent retrievers trap the clot or aspiration catheters suction it out.
- Restoration: Blood flow is quickly restored, minimizing damage.
Key Points
- Urgency: Especially for stroke, speed is critical, often within hours of symptom onset.
- Benefit: Significantly improves outcomes and reduces disability by restoring circulation.
- 다음글
- 다음글이 없습니다.
 ★Nventric_Brochure_1014.pdf (7.3 MB)
★Nventric_Brochure_1014.pdf (7.3 MB)